Electrical Energy Storage – Batteries, Smart Grids & EV Integration
Batteries are a cornerstone of the future energy market. Leading automation companies such as Panasonic, Siemens, and Samsung, along with specialized battery manufacturers like Leclanché and Varta, are investing heavily in this sector. Market forecasts anticipate significant growth over the next decade, driven by innovation and rising demand.
Concept
Electrical energy storage is already proving successful in managing the grids of smaller networks, demonstrating its reliability and scalability. With the growing adoption of private solar photovoltaic (PV) systems for homes and the entry of new players into the storage market, the demand for storage batteries is expected to increase substantially.
A typical Electrical Energy Storage (EES) customer is equipped with a photovoltaic (PV) installation connected to the grid. This setup provides the dual benefit of storing solar energy generated by the PV system and selling excess electricity back to the grid. Additionally, customers can store or draw energy directly from the grid as needed, ensuring flexibility, reliability, and optimised energy usage.
Home installation
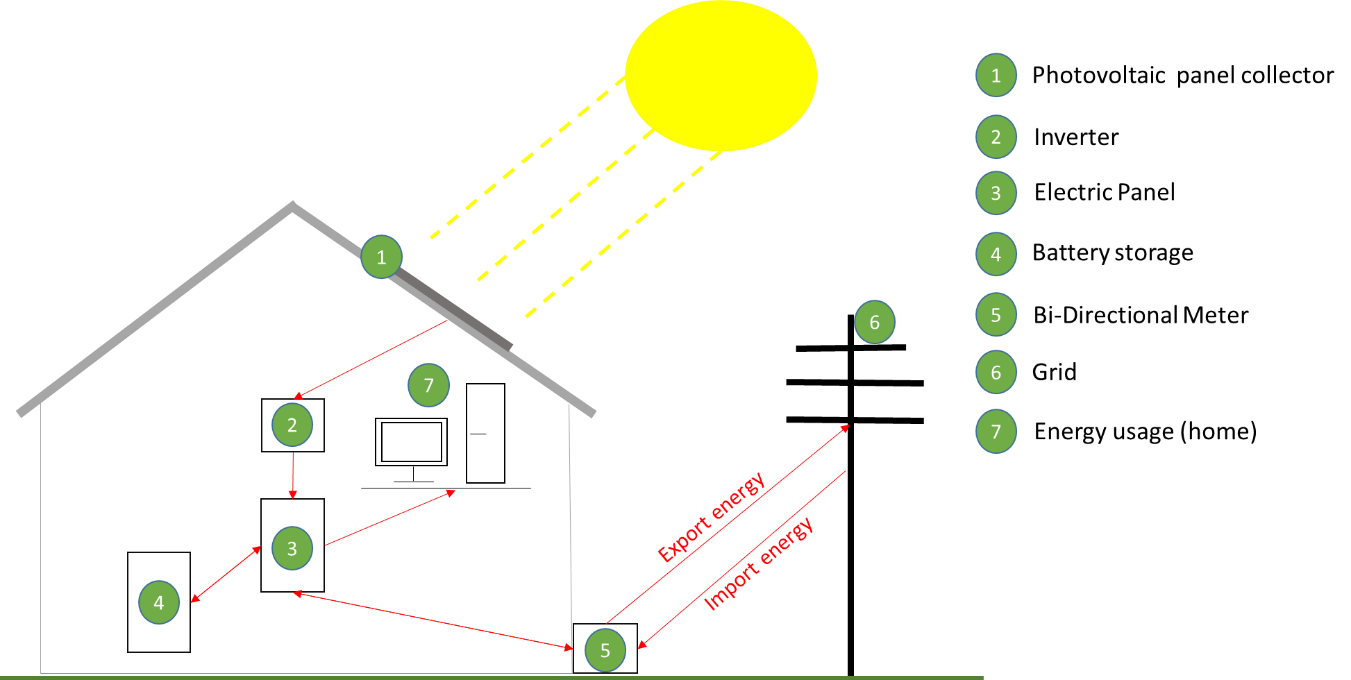
| Nb. | Components | Descriptions |
| 1 | Photovoltaic panel collector | A Photovoltaic panel collector installed on the roof of a house. Ideally directed on the south side of the house to increase the efficiency. |
| 2 | Inverter | This is an AC/DC inverter to convert the DC energy produced from the Solar panel to be used in AC for home usage. |
| 3 | Electric Panel | Electric Panel regulate the electricity and divert electricity according to demand directly to the house sockets for home usage, to the battery storage or back to the grid. |
| 4 | Battery storage | This is the electrical energy storage battery which is capable to store Photovoltaic produced electricity or energy from the grid. |
| 5 | Bi-Directional Meter | This is the meter managing the export and import of energy to the grid. This bi-directional meter is here to calculate the quantity used and sold (import and export). |
| 6 | Grid | The grid is the electrical network used to deliver electricity from energy distributor to consumers. In this picture the network is used to import and export energy. |
| 7 | Home usage | Energy usage for home appliances (Ex: Lamps, TV, Fridge…). |
Risks
- Batteries costs
- Space of the batteries
- Efficiency with the energy transfer of the batteries
- Duration: Durability of the batteries with the lifecycle usage of the batteries
- Environmental footprint of the battery production
Market Drivers
- Battery price reduction
- Energy price increase
- Government support with purchase subside or tax reduction
- Positive sales evolution of PV
- Positive sales evolution of EV
